1a inset measures the value of membrane potential relative to the extracellular space. Only neurons and muscle cells are capable of generating an action potential.
Depolarization Hyperpolarization Neuron Action Potentials Article Khan Academy
During an action potential ions cross back and forth across the neurons.
. Because the number of Na ions moved outside the cell is greater than the number of K ions moved inside the cell is more positive outside than inside. What has been described here is the action potential which is presented as a graph of voltage over time in. This test has 206 possible points but will be scored out of 200.
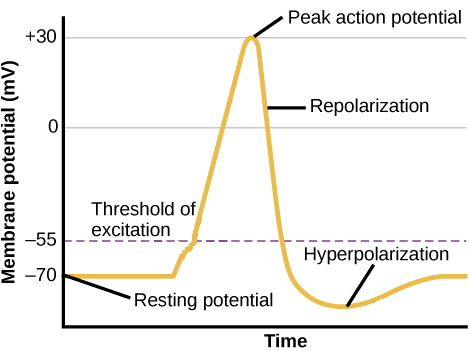
When there is a resting potential the outside of the axon is negative relative to the inside. Key facts about the action potential. In physiology an action potential AP occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls.
Once an action potential is triggered the membrane potential goes through a stereotypical sequence of. Opens or closes depending on. An action potential is defined as a sudden fast transitory and propagating change of the resting membrane potential.
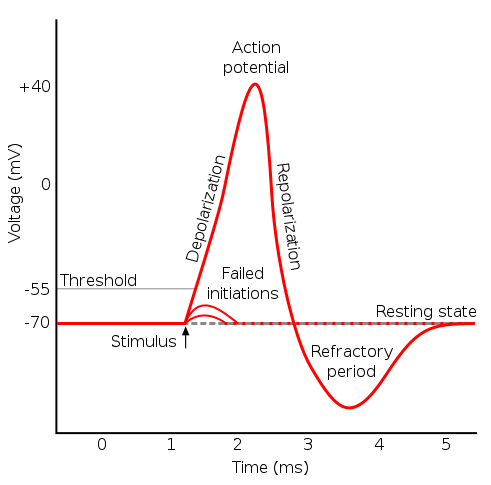
An action potential is described as a sudden and spontaneous change or reversal in the membrane potential above a threshold value due to increased permeability of the cell membrane. The speed of electricity regardless of the size of the axon. Action potentials are considered an all-or nothing event in that once the threshold potential is reached the neuron always completely depolarizes.
It is a large depolarization along the cell body that reaches the axon. That property is called the excitability. An action potential is a brief only a few milliseconds reversal of the membrane potential Vm.
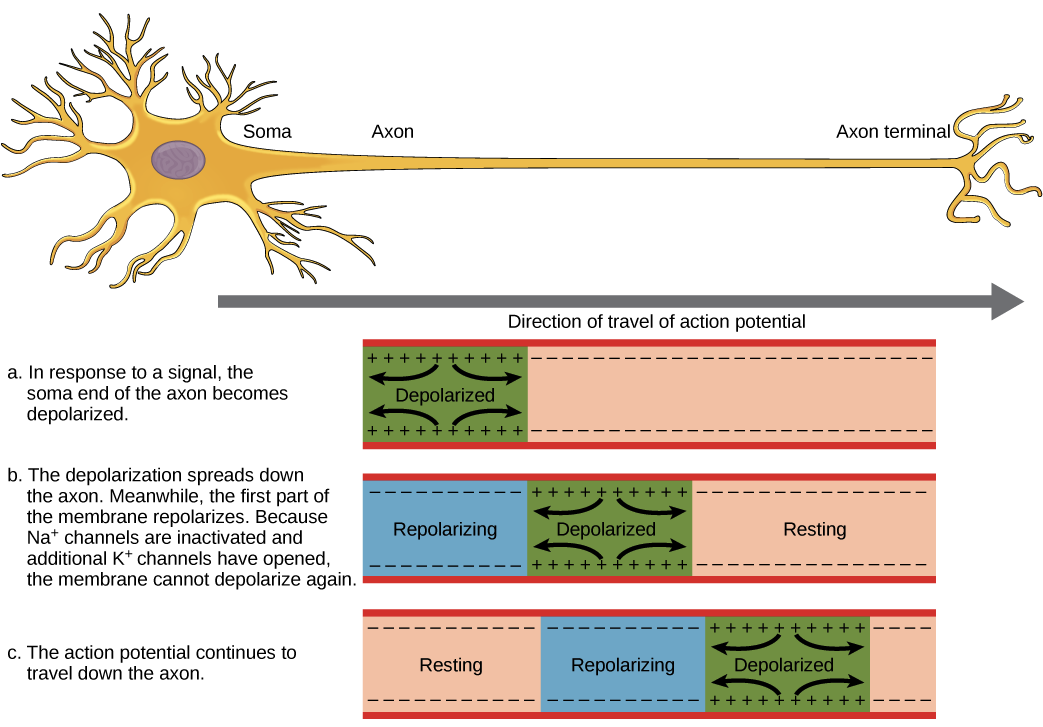
When a stimulus reaches a resting neuron the neuron transmits the signal as an impulse called an action potential. The action potential from the presynaptic neurons axon jumps to and continues to propagate down the postsynaptic neurons axon. This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize.
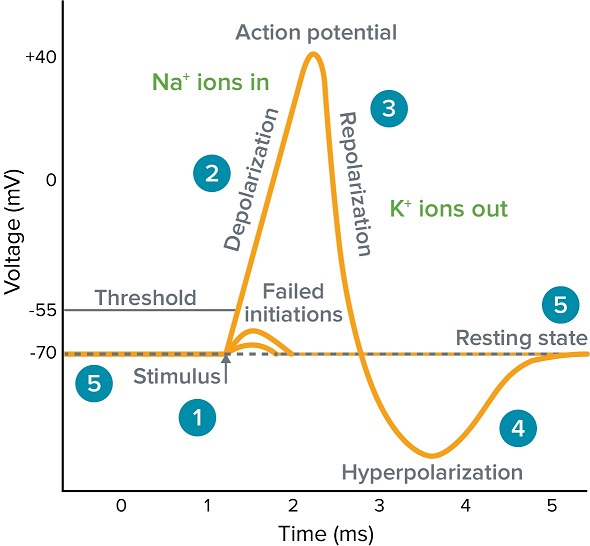
Biology I II. Each ion sodium potas-sium and chloride are usually considered has its own equilibrium potential. During an action potential Na ions diffuse out of the axon.
At rest the Vm of a neuron is around 70 mV closer to the equilibrium potential for potassium VK but during an action potential Vm transiently approaches 50 mV closer to the equilibrium potential for. K ions diffusing out of the axon repolarizes it. Voltage-gated sodium channels to open and sodium to flow with its electrochemical gradient.
The NaK ATPase reverses the pumping of ions across the membrane. The hyperpolarization phase of an action potential in an axon. The nervous impulse is referred to as the action potential.
Sodium channels open up to allow diffusion of Na inside stimulated area thereby depolarisation of membrane takes place. Action Potential Epilepsy 191 ACTION POTENTIAL EPILEPSY Directions for Teachers SYNOPSIS. It is the electrical signal that nervous tissue generates for communication.
If it reaches the axon the graded potential can lead to an action potential. Impulses in the axon travel towards the cell body. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells called excitable cells which include neurons muscle cells endocrine cells and in some plant cells.
The speed of an action potential down an unmyelinated axon is best described as ____. Less than 1 meter per second regardless of the size. The change in the membrane voltage from -70 mV at rest to 30 mV at the end of depolarization is a 100-mV change.
Graded potential refers to a membrane potential which can vary in amplitude. In a reflex arc when an opposing antagonistic muscle responds in the opposite fashion to another muscle on that same limb. Bio 449 Fall 2013 Name.
The basic properties of the action potential can be studied using a microelectrode constructed from a glass capillary tube with a fine tip and containing artificial intracellular solution. It is the electrical signal that nervous tissue generates for communication. Na ions are pumped out of the cell while K ions are pumped in.
Impulse transmission can take place only after the development of action potential from resting potential. It is the electrical signal that nervous tissue generates for communication. It is the electrical signal that nervous tissue generates for communication.
The context of a negative feedback loop the liver would best be described as a. The action potential is the nerve impulse. Na and Cl-ions rush into the cell and are then pumped out.
It is predominately established by the activity of sodium and potassium leak channels. Asked Feb 4 2019 in Psychology by mlwelsh. Once depolarization is complete the cell must now reset its membrane voltage back to the resting potential.
An axon that is more negative than the resting membrane potential is said to be _______. What has been described here is the action potential which is presented as a graph of voltage over time in Figure 1257. To accomplish this the Na channels close and cannot be opened.
Nations rush into the cell followed by the release of Kions. Permeability of the membrane translates to the action of the ion channels in allowing certain ions to enter the cell which would otherwise not be possible in the normal resting stage. The change in the membrane voltage from 70 mV at rest to 30 mV at the end of depolarization is a 100-mV change.
The minimum voltage that is required to generate an action potential is called the _______. What has been described here is the action potential which is presented as a graph of voltage over time in Figure 7. This microelectrode inserted into the cell body or axon of a neuron Fig.
It is a nongraded all-or-none event meaning that the magnitude of the action potential is independent of the strength of the depolarizing stimulus that produced it provided the depolarization is sufficiently large to reach threshold. Action potentials - the rapid change in potential difference across the membrane - caused by the change in permeability of the membrane to Na and K ions - voltage gated channels for Na and K ions. The resting potential can be described as follows.
Which of the following statements best describes the graded potential. It can be described as reversal of negative membrane potential in positive membrane potential also called action potential. An action potential requires _______.
Which of the following best describes an action potential in a neuron. Action potential refers to a change in the electrical potential which is associated with the transmission of impulses along the membrane of a nerve cell or muscle cell.
What Is An Action Potential Action Potential Chart Membrane Potential Molecular Devices

Action Potential The Resting Membrane Potential Generation Of Action Potentials Teachmephysiology
Depolarization Hyperpolarization Neuron Action Potentials Article Khan Academy
0 Comments